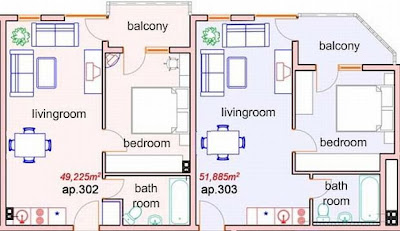
Flat or apartmentAn apartment is a self-contained housing unit that occupies only part of a building. Apartments may be owned (by an owner/occupier) or rented (by tentants).
A common alternative term for apartment is flat. The term apartment is favored in North America, whereas the term flat is commonly, but not exclusively, used in the United Kingdom.
Most apartments are in buildings designed for the purpose, but large older houses are sometimes divided into apartments. The word apartment connotes a residential unit or section in a building. In some locations, particularly the United States, the word denotes a rental unit owned by the building owner, and is not typically used for a condominium.
In the UK, some flat owners own a share in the company that owns the freehold of the building. This is commonly known as a "share of freehold" flat. The freehold company has the right to collect annual ground rents from each of the flat owners in the building. The freeholder can also develop or sell the building, subject to the usual planning and restrictions that might apply.
Apartment types and characteristicsApartments can be classified into several types. The apartment usually consist mainly of a large room which is the living, dining, and bedroom combined. That rooms can also be built separately. There can be usually kitchen facilities as part of a central room, but the bathroom is always its own smaller separate room.
Moving up from the efficiencies are one-bedroom apartments, in which one bedroom is separate from the rest of the apartment. Then there are two-bedroom, three-bedroom, etc. apartments. Small apartments often have only one entrance.
This is a typical flat or apartment:
Terraced house
A terrace(d) or row house is a style of medium-density-houses that originated in Europe in the late 17th century, where a row of identical or mirror-image houses share side walls. The first and last of these houses is called an end terrace, and is often larger than those houses in the middle.
In the UK, the first streets of houses with uniform fronts were built by Nicholas Barbon in the rebuilding after the Great Fire of London. The Georgian idea of treating a row of houses as if it were a palace front, giving the central houses columned fronts under a shared pediment, appeared first in London's Grosvernor Square and in Bath's Queen Square.
By the early Victorian period, a terrace had come to designate any style of housing where individual houses repeating one design are joined together into rows. The style was used for workers' housing during the great industrial boom following the industrial revolution, particularly in the houses built for workers of the expanding textile industry. The terrace style spread widely in the UK, and now it's the most typical type of house in the United Kingdom.
The typical terraced houses in London:

Detached house
A detached house is a free-standing residential building. Most single-family homes are built on lots larger than the structure itself, adding an area surrounding the house, which is commonly called a yard in North American English or a garden in British English. Garages can also be found on most lots. In older homes, they are typically detached, standing as a separate building, either near a driveway or facing an alley in urban areas.
Rooms
Living room: also called the lounge or the dining room in the UK; other terms used in the UK are sitting room and drawing room, the latter now generally only in grander old style properties): It's usually the largest room of the house, used for relaxing and entertaining guests.
Kitchen: Food preparation is done here. Some homes feature eat-in kitchens where the family has their meals in the same room as the food is prepared in.
Bedroom: Any type of house features at least one bedroom providing a space to sleep.
Bathroom: The room where grooming is taken care of, containing a bathtub and possibly a shower. It may be combined with a toilet and include a sink or washbasin.
Types of detached house
Cotagge: a small house. In the UK and Ireland they small, old (especially pre World War I) house in a rural or formerly rural location whether with one, two or (rarely) three storeys is a cottage.
Bungalow: In British English it refers to any single storey house (which are much rarer in the UK than the U.S.)
Villa: a term originating from Roman times, when it was used to refer to a large house which one might retreat to in the country. In the late 19th and early 20th century villa suggested a freestanding comfortable sized house, on a large block, generally found in the suburbs.
Mansion: a very large house, usually of more than one story, on a very large block of land or estate.
This is a typical detached house in the UK:
Semi-detached house
Semi-detached housing (often abbreviated to semi in the UK and a duplex in New England), consists of pairs of houses built side by side as units sharing a party wall and usually in such a way that each house's layout is a mirror image of its twin. This style of housing, although built throughout the world, is commonly seen as particularly symbolic of the suburbanisation of the United Kingdom.
This type of housing can be thought of as being a half-way state between terraced housing and detached homes. Terraced housing is constituted by continuous row houses with open spaces at the front and back, while semi-detached houses have front, rear and any one side open spaces, and individual detached houses have open spaces on all sides.
During the house price boom in the years to 2004 many UK property developers found they could create value by demolishing semi-detached houses and building two detached houses on the same site, often with a very narrow gap between the new units.
This is a typical semi detached house in the UK:

And the plan of the house: